Spotlights
Biological Science Laboratory Technician (Biological Science Lab Tech), Biological Science Technician, Laboratory Technician, Marine Fisheries Technician, Research Assistant, Research Associate, Research Specialist, Research Technician, Wildlife Biology Technician, Biotechnology Technician, Environmental Technician, Microbiology Technician, Biotechnology Laboratory Assistant
Have you ever taken a laboratory class, or seen a lab environment in a movie or TV show? If so, you know that labs are tidy, organized places where experiments are conducted and results are observed.
There are many different lab types, but the medical research lab is one of the most common. Medical researchers – usually biologists and scientists – frequently need help from assistants known as Biological Technicians. These assistants run tests and experiments, capture data, study results, and report their findings.
They also keep labs clean and stocked with supplies, maintain equipment, protect samples from contamination, and utilize data analysis programs. Some work with lab animals or go out to collect biological specimens in the field. By managing these tasks, Biological Technicians directly contribute to scientific discoveries related to fields such as environmental research, genetic studies, and drug development.
Biological Technicians may work for universities, government agencies, or private industry employers. They must follow strict protocols, wear appropriate personal protective equipment, and safeguard the data and collections under their care.
- Contributing to groundbreaking scientific research
- Working in a hands-on, lab-based environment
- Supporting advancements in medical, agricultural, and environmental sciences
- Enjoying job stability with a growing demand for biological research
Working Schedule
Biological Technicians tend to work full-time, with overtime possible to meet deadlines. They usually work in laboratories but may also take trips to field sites.
Typical Duties
- Conduct and assist in various types of medical research.
- Assist in the design, preparation, and execution of lab experiments, following regulatory and safety protocols.
- Set up, adjust, calibrate, clean, and troubleshoot lab and field equipment.
- Order and maintain supplies and equipment.
- Ensure work areas are clean, organized, and prepared.
- Collect biological samples. Handle samples carefully to ensure their integrity and avoid contamination.
- Measure and prepare compounds, solutions, reagents, and animal feed for lab procedures.
- Prepare, isolate, and examine specimens to detect diseases or analyze biological properties.
- Run tests to determine the physical and chemical properties of substances.
- Feed and care for laboratory animals, if applicable.
- Monitor experiments and collect data. Use software to record, analyze, and interpret data.
- Create data-driven reports. Maintain records of activities. Input data into databases.
Additional Duties
- Provide technical support to researchers, as needed.
- Review articles or scientific literature to support ongoing projects and keep up to date on advancements.
- Train new lab assistants.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment at all times.
Soft Skills
- Analytical thinking
- Attention to detail
- Communication
- Curiosity
- Focus
- Integrity
- Organizational skills
- Patience
- Problem-solving
- Teamwork
- Time management
Technical Skills
Biological Technicians need hard skills related to the following:
- Laboratory techniques and procedures (e.g., sterilization and sample preparation)
- Data analysis and statistical software (Excel, R, and laboratory management software)
- Data entry
- Field sample and specimen collection (spectrophotometers, microscopes, and PCR machines)
- Laboratory instruments and equipment
- Health, biological, and chemical safety protocols
- Microscope operation
- Technical writing and documentation
- Biological sample preparation and handling
- Animal caretaking
- Research institutions
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Colleges and universities
- Government agencies
- Environmental consulting firms
Biological Technicians are expected to perform their duties with precision, adhering to established protocols to ensure the reliability of their findings. This attention to detail demands focus and diligence because even small mistakes can destroy the validity of an experiment. Accuracy and quality assurance are therefore essential.
The work can be challenging and even frustrating sometimes because experiments don’t always produce the desired results. Biological Technicians have to be patient and resilient, often repeating procedures over and over to validate findings.
Safety is another critical aspect of the job since there is a risk of exposure to hazardous chemicals or biological specimens. Everyone in the lab has to prioritize safety, strictly follow protocols, wear appropriate protective gear, and avoid making mistakes that could have harmful consequences. They also have to be up to speed on contingency plans in the event of an emergency.
Lab workers increasingly use AI, automated processes, and specialized software to streamline data collection and analysis, so they can handle larger datasets and deliver results more efficiently. This ultimately enhances the scope and impact of the work they’re doing!
The demand for genetic testing, environmental monitoring, and biomedical research has grown in recent times, creating new opportunities for research studies. In addition, technicians are increasingly involved in work that addresses healthcare outcomes, environmental degradation, and other global challenges.
Meanwhile, many labs are adopting more eco-friendly practices, such as minimizing waste and using renewable materials, to contribute to sustainability efforts.
Biological Technicians may have enjoyed hands-on projects like school science experiments, gardening, or observing nature. They often excelled in biology, chemistry, and other science courses.
- A bachelor’s degree in biology or a closely related field, such as biochemistry, molecular biology, or environmental science, is typically required. Common courses include:
- Biology and Chemistry (including organic and inorganic chemistry)
- Microbiology and Cell Biology
- Data Analysis and Statistical Methods
- Environmental Science (especially for roles in ecology or conservation)
- Laboratory coursework for gaining practical experience
- Internships or research assistant roles can provide valuable hands-on experience. Other helpful skills and experience include:
- Experience with specialized equipment, such as spectrophotometers, microscopes, and PCR machines
- Familiarity with data analysis tools, including Excel, R, and laboratory management software
- Safety protocols for handling hazardous materials and biological specimens
- Relevant optional certifications include:
- American Association for Laboratory Animal Science - Laboratory Animal Technician
- American Fisheries Society - Fisheries Professional Associate
- National Drug and Alcohol Screening Association - Certified Professional Collector
- National Registry of Environmental Professionals - Associate Environmental Professional and Registered Environmental
Laboratory Technologist
- Additionally, certifications related specifically to laboratory safety, handling biological materials, lab software, and data analysis tools may come in handy!
- Look for accredited science programs featuring laboratory components, facilities with modern equipment, internships and co-op research opportunities, and experienced faculty members.
- Compare tuition and fees costs, noting in-state vs. out-of-state costs.
- Review scholarship and financial aid options.
- Check out graduation and job placement statistics.
- In high school, take advanced courses in biology, chemistry, and math to prepare for college-level training programs.
- Participate in science fairs or join science clubs.
- Develop analytical skills through data projects or related coursework.
- Volunteer, intern, or get a part-time job at a lab or environmental organization.
- Read books and articles related to medical lab work.
- Ask to do an informal interview with a working Biological Technician.
- Keep track of work and academic accomplishments for your resume and/or college applications.
- Attend career fairs and industry events to grow your network and learn about career paths.
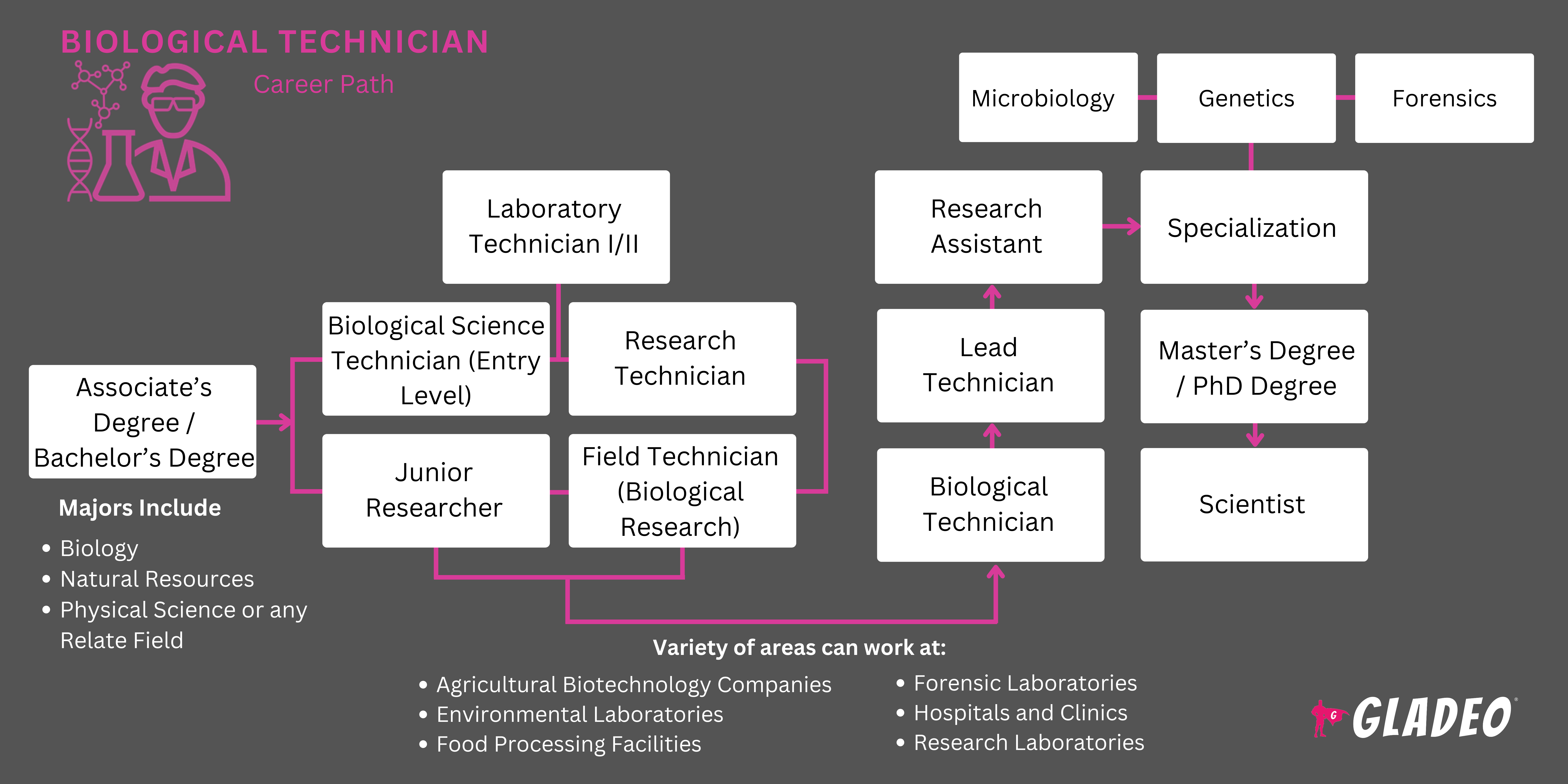
- Scan job portals like Indeed.com, Glassdoor, ZipRecruiter, and other sites.
- Review job ads and look for keywords to list on your resume, such as:
- Cell culture
- Data analysis
- DNA extraction
- Environmental sampling
- Gel electrophoresis
- Laboratory safety protocols
- Microscopy
- Molecular biology
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
- Protein purification
- Quality control
- Scientific instrumentation
- Specimen preparation
- Statistical software (e.g., R, SPSS)
- Check out Biological Technician resume templates for ideas.
- Read sample interview questions such as “How do you ensure accuracy and reliability in your data collection and analysis during laboratory experiments?” or “Can you describe how you would handle unexpected results in a research experiment, and what steps you would take to troubleshoot the issue?”
- Practice your replies via mock interviews.
- Reach out to your professional network to ask for tips about job openings.
- Ask former professors and supervisors to write recommendation letters or request their consent to list them as references.
- Make a profile on LinkedIn and other networking platforms to advertise your availability.
- Keep up with current developments related to the industry. Be familiar with the terminology before going into interviews.
- When you get called for an interview, research the employer to learn more about them.
- Dress appropriately for job interviews!
- Talk with your supervisor about additional certifications and specialized training you could complete to qualify for advancement.
- Participate in workshops or webinars. Attend industry conferences and network with scientists and researchers.
- Join professional organizations like the American Society for Microbiology.
- Take on new lab responsibilities and specialize in a niche (e.g., genetics, environmental biology, forensics, etc.).
- Learn how to use more advanced laboratory software and data analysis tools, including AI tools.
- Seek out advanced research roles or consider earning a master’s degree.
- Practice diligent sanitation procedures. Ensure instruments and equipment are cleaned as appropriate.
- Read equipment manuals and become a subject matter expert on the machines you use.
- Keep supplies stocked and equipment well maintained.
- Anticipate problems and be proactive in preventing them.
- Stay informed on trends and advancements in the biological sciences, as well as regulatory changes.
- Volunteer to mentor or train new hires to demonstrate leadership skills.
- Publish research findings in industry journals to build credibility and recognition.
- Participate in cross-disciplinary projects to broaden your skill set. Collaborate with external organizations or agencies on joint projects.
- Volunteer for fieldwork or off-site research projects to gain diverse experiences.
- Build relationships with senior staff and seek their guidance for advancement opportunities.
- Gain proficiency in grant writing to support research funding efforts.
- Create a professional portfolio that highlights your skills, certifications, and contributions.
- Consider relocating or switching employers if necessary to achieve career goals. States with the highest employment levels for Biological Technicians include California, Massachusetts, New York, Texas, and Maryland.
Websites
- American Academy of Forensic Sciences
- American Association for Laboratory Animal Science
- American Chemical Society
- American Fisheries Society
- American Institute of Biological Sciences
- American Society for Cell Biology
- American Society for Clinical Pathology
- American Society for Microbiology
- American Society of Plant Biologists
- Association for Biology Laboratory Education
- Association for Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine
- Association of Genetic Technologists
- Bio-Link
- Biophysical Society
- Botanical Society of America
- DIYbio
- Ecological Society of America
- Entomological Society of America
- Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology
- Genetics Society of America
- Institute of Food Technologists
- International Society for Computational Biology
- Marine Biological Laboratory
- National Association of Biology Teachers
- National Center for Biotechnology Information
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- National Institutes of Health
- Society for Conservation Biology
- Society for Freshwater Science
- Society for In Vitro Biology
- Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry
- Society of Integrative and Comparative Biology
- Society of Toxicology
- The ISME Journal
- The Paleontological Society
- Wildlife Society
Books
- Biology Laboratory Manual, by Darrell Vodopich and Randy Moore
- Medical Laboratory Science Review, by Robert R. Harr MS MLS (ASCP)
- Molecular Biology of the Cell, by Bruce Alberts, et. al.
Biological Technicians are important front-line members of the medical research community, but there are plenty of other professions to consider if this career isn’t resonating with you. Check out our list below for some ideas!
- Agricultural Scientist
- Biochemist
- Bioinformatics Specialist
- Biological Scientist
- Biomedical Engineer
- Bioprocessing Technician
- Botanist
- Calibration Technologist
- Chemical Technician
- Conservation Scientist
- Cytogenetic Technologist
- Ecologist
- Environmental Science Technician
- Environmental Scientist
- Epidemiologist
- Food Safety Specialist
- Food Science Technician
- Forensic Science Technician
- Geneticist
- Histotechnologist
- Marine Biologist
- Medical Laboratory Technician
- Microbiologist
- Molecular Biologist
- Nanotechnology Engineering Technologist
- Pharmacologist
- Plant Science Technician
- Toxicologist
- Veterinary Technician
- Wildlife Biologist
- Zoologist
Newsfeed
Featured Jobs

Online Courses and Tools








