Spotlights
Freight Maintenance Specialist, Locomotive Repairman, Rail Car Maintenance Mechanic, Rail Car Mechanic, Rail Car Repairman, Rail Car Sandblaster, Rail Car Welder, Railroad Car Repairman, Train Car Repairman
Since their widespread adoption in the US, railroads have transformed our country in amazing ways. From easier interstate travel to the crucial transportation of goods, our society (and economy!) have come to rely heavily on the vast network of steel rails crisscrossing the nation. Upon these tracks, mighty rail cars of all shapes and sizes speed along, some pulled by locomotives as part of a connected train, others self-propelled.
Like any vehicle, rail cars require plenty of maintenance and repairs, which is where Rail Car Repairers come into the picture! Generally employed by railroads or transit companies, they work on a broad assortment of rail car types including autoracks, boxcars, center beams, hoppers, coil cars, flatcars, gondolas, tank cars, well cars, and more. The job isn’t easy; it can require lots of heavy lifting, handling greasy parts and equipment, and in some cases welding. As they say, “it’s a dirty job but somebody’s gotta do it” — and luckily, Rail Car Repairers can earn a great income in this often-overlooked profession!
- Ensuring the timely transportation of vital goods to all parts of the country
- Helping goods flow so the economy can keep going
- Contributing to lowering harmful emissions (since trains are overall more eco-friendly than many other forms of transportation)
Working Schedule
- Rail Car Repairers usually work full-time, with overtime needed in some cases to ensure work is completed within timeframes. Nights, weekends, and holiday shifts may be required.
Typical Duties
- Conduct thorough visual inspections of rail car exteriors and structural components
- Perform routine service maintenance on rail car vehicles in accordance with manufacturer or other guidelines, including replacing bearings, pistons, gears, etc.
- Keep track of maintenance work via records
- Inspect and replace worn-out or damaged mechanical components
- Make adjustments, alignments, or modifications, as needed, to keep vehicles operating at peak efficiency
- Take measurements to fabricate parts or components
- Paint rail car surfaces to prevent corrosion. Seal cracks and gaps, apply weather stripping
- Repair roofs, flooring, walls, steps, etc.
- Drive rail cars to move them around short distances
- Double-check work to ensure repairs are done properly
- Install new parts and fixtures
- Troubleshoot, repair, and rewire basic electronics for controls and brake systems
- Keep rail car bodies, parts, and windows clean
- Repair upholstery
Additional Responsibilities
- Wear assigned protected gear and follow safety protocols
- Lift and carry heavy parts
- Weld or fabricate parts, as needed
- Train and supervise other team members
- Stay on top of changes and technological advancements
Soft Skills
- Adaptability
- Attention to detail
- Critical thinking
- Independence
- Innovative
- Monitoring
- Persistent
- Problem-solving
- Safety-oriented
- Stress tolerance
- Strong communication skills
- Visualization
Technical Skills
- Familiarity with hand tools, torque wrenches, welding equipment, pneumatic hoists, jacks, pinch bars, cutting torches, micrometers, ammeters, roofing materials, cement, nails, paint, wiring, insulation, plumbing, window sash frames, attach weather stripping, gauges, turnbuckles, and wrenches, and more
- Knowledge of welding
- Mechanical aptitude
- Physical stamina and strength
- Quick reaction time
- Steady hands and manual dexterity
- Manufacturers
- Public/private transit companies
- Railroads
Rail Car Repairers are expected to keep things moving because rail cars are so essential for the transportation of goods. Everything from hazardous materials and bulk cargo (such as iron ore and coal) to consumer goods (like furniture, automobiles, electronics, and foodstuffs) is shipped by rail freight. Without those shipments, the economy becomes severely disrupted.
As a result, overtime may be needed to get things back on track (no pun intended) when problems arise! Workers may need to endure inclement weather conditions, as well as long commute times in some cases.
Passenger railroad usage is rising again because it's an inexpensive method of travel, especially for long distances when a bus might be uncomfortable and airfare too costly. This should increase demand for Rail Car Repairer services. Meanwhile, autonomous trains are making a splash thanks to "real-time data transmission systems and advanced sensor technology." The rail industry is also adding the Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence to its modern toolbox, too.
On an environmental note, the railway sector is striving to contribute to decarbonization efforts, doing its part to reduce emissions impacts on the climate. It remains to be seen the full extent that other emerging trends will have on the role of Rail Car Repairer workers.
To say that Rail Car Repairers grew up playing with toy trains would just be speculation. But it’s probably true they enjoyed working with their hands and didn’t mind getting dirty. They could have been adept at doing a wide range of tasks, including some that were labor-intensive. They may have been comfortable working or tinkering by themselves outdoors or with mechanical contraptions indoors. It’s possible they also liked sports or physical exercise since Rail Car Repair takes both stamina and strength!
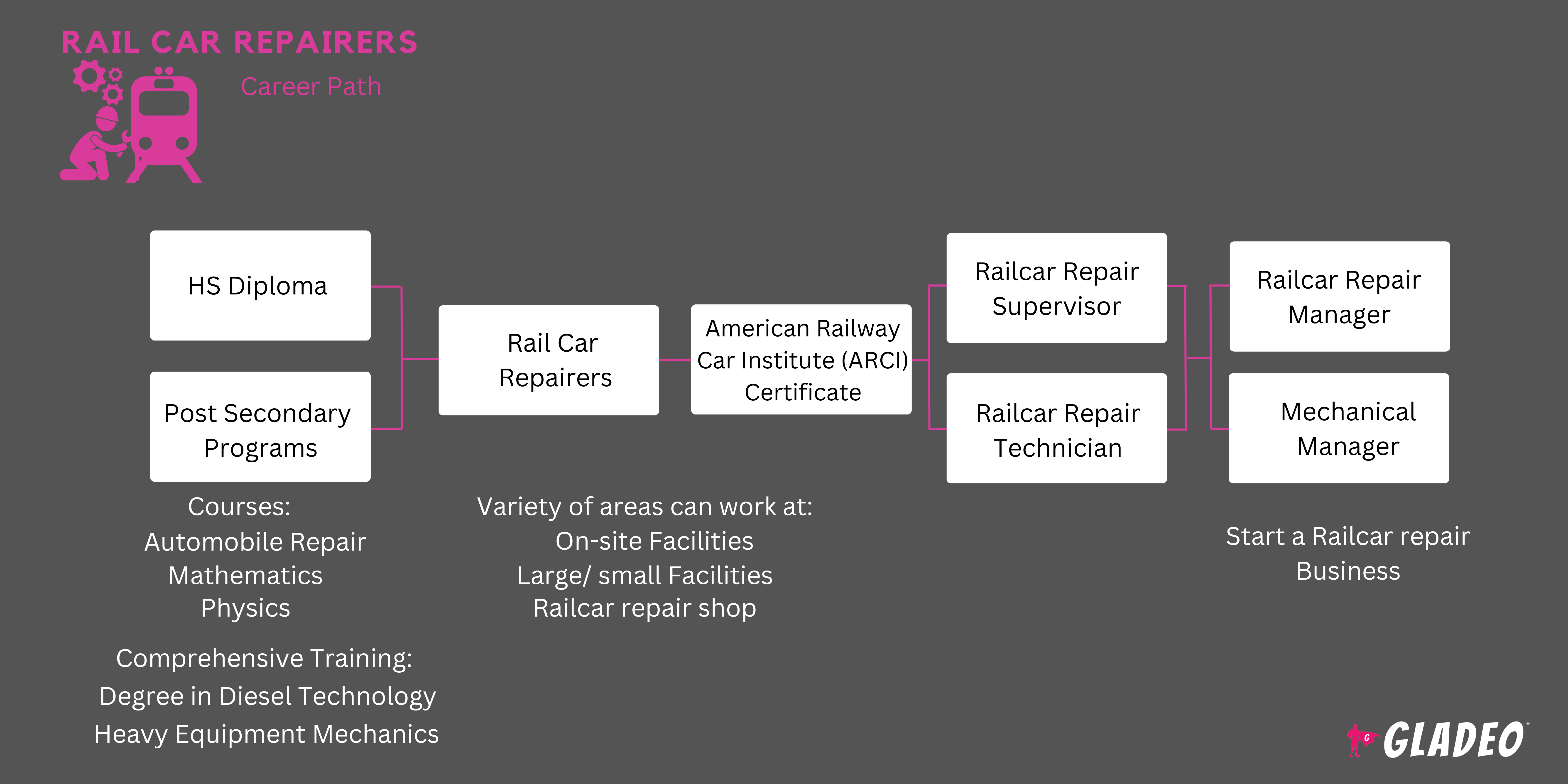
- Rail Car Repairers usually have a high school diploma or equivalent, but don’t need a college degree
- Per CareerOneStop, 47% of workers in this field hold a high school diploma or equivalent, while 12% hold less. 23% have “some college, no degree” while 13% have an associate's degree.
- Many learn through on-the-job training or apprentice programs
- Employers may give preference to those with a fair amount of welding experience
- Welder journeyman training can take up to three or four years, after which a state licensure exam must be passed
- A commercial driver’s license may also boost one’s competitiveness
- Candidates might have to pass a criminal and drug background check plus a physical examination
- Rail Car Repairers don’t usually have degrees but they can complete vocation training to learn some mechanic, electrical, and welding skills
- Most applicable classes for these subjects are best taught in-person versus online
- Sign up for HS classes in math, science, shop, drafting, computer science, and physical fitness
- Consider taking a local community Welding Technology program and mechanics courses
- Gain part-time work experience in an automotive garage or site where you can work on heavy equipment
- Write down the names and contact info of people who might serve as future job references
- Study books, articles, and video tutorials related to different job tasks of a Rail Car Repairer
- Ask a local railroad or transit company if you can shadow a Rail Car Repairer for a day
- Keep track of the skills you develop and the tools you learn how to use
- Start drafting your resume early and keep adding to it as you go, so you don’t lose track of anything
- Finish relevant certifications when you can to bolster credentials and make you more competitive in the job market
- Research applicable unions and any available training or work opportunities they have in your area (see our Resources > Websites tab)
- Post your resume on job portals such as Indeed, Simply Hired, Glassdoor, and Zippia
- You may or may not need a formal resume to apply, but check out Rail Car Repairers resume templates anyways for ideas for wording and formats
- List all education, skills, training, and work history on your resume
- Search for openings on the websites of companies you want to work for
- Apply for entry-level positions and work your way up
- Always do your best at any job you hold and ask former supervisors if they will provide a personal reference for you. Don’t catch them off guard by giving out their contact info without permission
- Reach out to working Rail Car Repairers to ask for job-seeking tips
- Make an account on Quora to ask job advice questions from workers in the field
- Move to where the most job opportunities are! The states with the highest employment levels for Rail Car Repairers are Illinois, Texas, Virginia, Ohio, and Pennsylvania. The highest concentration of jobs are in Wyoming, Nebraska, Illinois, Mississippi, and Arkansas
- If you take college classes, ask your school’s career center for help connecting with recruiters
- Study common interview questions to prepare ahead of time
- Dress professionally for job interviews!
- Rail Car Repairers can move up and earn more by being on time, doing solid work, demonstrating leadership and accountability, and enhancing or adding to their existing skills
- Stay on top of the changes in technology through online or vocational courses
- Build your reputation as a worker who is accountable, reliable, and innovative
- Learn all you can from more senior Rail Car Repairers, and try to work on different types of vehicles
- Mentor new employees and help them stay motivated and safe
- Make strong connections in your company and treat people with respect
- Do your best to earn recognition or awards that can help enhance your professional reputation
- Schedule a conversation with your supervisor to discuss opportunities for advancement
- Company loyalty is important but considers applying to new jobs with more promotion potential, if necessary to advance
- Participate in union activities and events. Unions can help workers negotiate for better wages, benefits, safety, and training, so participation may be important for moving up
Websites
- American Railway Engineering and Maintenance-of-Way Association
- American Welding Society
- Associated Equipment Distributors
- Brotherhood of Locomotive Engineers & Trainmen
- Brotherhood of Maintenance of Way Employees
- Brotherhood Railway Carmen
- International Association of Sheet Metal, Air, Rail and Transportation Workers
- International Brotherhood of Boilermakers, Iron Ship Builders, Blacksmiths, Forgers and Helpers
- International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America
- National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence
- National Railroad Construction and Maintenance Association
- Railroad Workers United
- RPCA Resource Library
- Sheet Metal Workers' International Association
- Transportation Communications International Union
- Transport Workers Union of America AFL-CIO
Books
- How To Weld (Motorbooks Workshop), by Todd Bridigum
- Train: The Definitive Visual History, by DK and the Smithsonian Institution
- Understanding Automotive Electronics, by William Ribbens
Rail Car Repair work can be labor-intensive and duty location options may be limited. The Bureau of Labor Statistics lists a few related occupations to think about, for those who still want to explore similar career paths.
- Aircraft and Avionics Equipment Mechanics and Technicians
- Automotive Body and Glass Repairers
- Bus and Truck Mechanics and Diesel Engine Specialists
- Diesel Service Technicians and Mechanics
- Heavy Vehicle and Mobile Equipment Service Technicians
- Industrial Machinery Mechanics
- Maintenance Workers, Machinery
- Millwrights
- Small Engine Mechanics
Newsfeed
Featured Jobs

Online Courses and Tools








